Introduction
Many workplaces rely too heavily on PPE. However, PPE is the last line of defense, not the first. The hierarchy of controls helps organizations manage risk effectively.
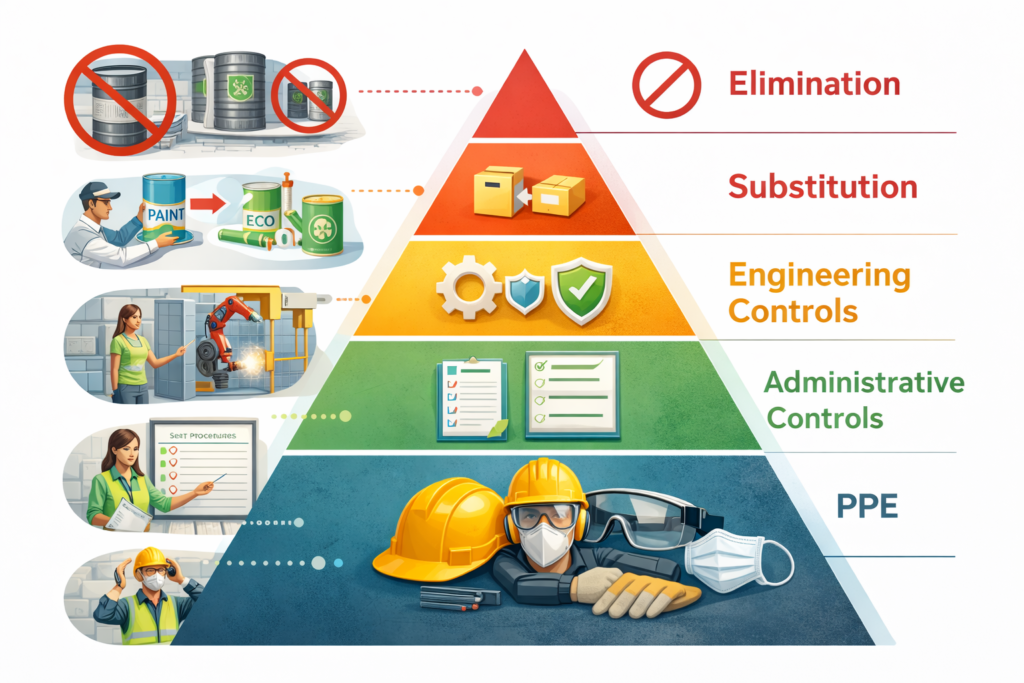
The 5 Levels of the Hierarchy of Controls
1. Elimination (Most Effective)
Remove the hazard entirely.
Example: Designing out work at height.
2. Substitution
Replace with something safer.
Example: Using water-based paint instead of solvent-based paint.
3. Engineering Controls
Isolate people from the hazard.
Example: Guardrails, machine guards, ventilation.
4. Administrative Controls
Change the way people work.
Example: Procedures, training, permits.
5. PPE (Least Effective)
Protect the worker directly.
Example: Helmets, gloves, respirators.
Common Mistake
Relying on PPE alone gives a false sense of safety.
Key Takeaway
Effective safety starts at the top of the hierarchy, not the bottom.
Famous Words of Inspiration...
"No matter how much cats fight, there always seem to be plenty of kittens."




